August 13, 2010
 by: Tami O’Connor
by: Tami O’Connor
Why do some objects float while others sink? Archimedes discovered that an object is buoyed upward with a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced. An object will float in a fluid whenever its weight is less than the weight of the fluid displaced; otherwise it will sink… So what does this mean in English??? An easier way to think about it is that an object that is less dense than the fluid it is in will rise to the top of the more dense fluid.
 In demonstrations of liquids of varying densities, the liquid with the greatest density will sink to the bottom of the container while the less dense liquid will remain on the top. There are wonderful demonstrations you can conduct with your class using immiscible liquids (liquids that do not mix) of different densities, and there are a number of high interest experiments your students can conduct using liquids of different densities. If you find this topic interesting, please visit the blog we wrote on the W-Tube.
In demonstrations of liquids of varying densities, the liquid with the greatest density will sink to the bottom of the container while the less dense liquid will remain on the top. There are wonderful demonstrations you can conduct with your class using immiscible liquids (liquids that do not mix) of different densities, and there are a number of high interest experiments your students can conduct using liquids of different densities. If you find this topic interesting, please visit the blog we wrote on the W-Tube.

Gasses also have varying densities, but in the elementary and middle school classrooms, students don’t often have the same opportunity to work with gasses as they would liquids, or more often, liquids and solids. Read the rest of this entry »
 Leave a Comment » |
Leave a Comment » |  Chemistry, density, Elementary level, experiments, Middle School level | Tagged: Archimedes Principle, buoyant force, density of gasses, phenomenon based learning, sink or float, solar tube, STEM |
Chemistry, density, Elementary level, experiments, Middle School level | Tagged: Archimedes Principle, buoyant force, density of gasses, phenomenon based learning, sink or float, solar tube, STEM |  Permalink
Permalink
 Posted by Tami O'Connor
Posted by Tami O'Connor
July 10, 2010
 by Ted Beyer
by Ted Beyer
One of my favorite authors, Arthur C. Clark, once said, “Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.” This has been quoted, misquoted and reused for years. Of course, it’s perfectly true, and magicians have been using science as part of their acts for centuries. Things that we take for granted today were once bleeding edge technology. I remember in high school reading that sometime ‘soon’ (this was more than 30 years ago) there would be TVs that would be so thin that they would hang on the wall like pictures – impossible! A generation before, the concept of television itself was astonishing, and a generation before that, moving pictures of any kind were magical.
As I started to think about this, I suddenly realized that there are many products that we sell here at Educational Innovations that are used – currently – by magicians as ‘tricks’ in their act. Let’s take a look…. Read the rest of this entry »
 Leave a Comment » |
Leave a Comment » |  Chemistry, College level, Elementary level, experiments, High School level, Middle School level, Physics | Tagged: discrepant event, eddy currents, ice melting blocks, Lenz's Law, magic, magic snow, Newton's Nightmare, nitinol wire, PBL, phenomenon based learning, slush powder, snow polymer, sodium polyacrylate |
Chemistry, College level, Elementary level, experiments, High School level, Middle School level, Physics | Tagged: discrepant event, eddy currents, ice melting blocks, Lenz's Law, magic, magic snow, Newton's Nightmare, nitinol wire, PBL, phenomenon based learning, slush powder, snow polymer, sodium polyacrylate |  Permalink
Permalink
 Posted by Tami O'Connor
Posted by Tami O'Connor
June 13, 2010
 by: Tami O’Connor
by: Tami O’Connor
When two 1-pound, 2-inch diameter, chrome steel spheres are smashed together, enough heat is generated at the point of contact to burn a hole in ordinary paper! This dramatic demonstration has been a favorite of students in every grade for as long as I have been teaching!
 There are a few considerations when allowing students (especially younger ones) to conduct this activity on their own… First, the spheres are pretty heavy, so if they were either dropped on a foot or onto a nice tile floor, the result would not be good. Also, be sure that the only thing between the spheres is paper or aluminum foil. Fingers caught between the colliding spheres would not be happy. Finally, all participants should wear safety glasses, as it is not unusual for a small piece of paper to fly off after the spheres collide.
There are a few considerations when allowing students (especially younger ones) to conduct this activity on their own… First, the spheres are pretty heavy, so if they were either dropped on a foot or onto a nice tile floor, the result would not be good. Also, be sure that the only thing between the spheres is paper or aluminum foil. Fingers caught between the colliding spheres would not be happy. Finally, all participants should wear safety glasses, as it is not unusual for a small piece of paper to fly off after the spheres collide.
Read the rest of this entry »
 2 Comments |
2 Comments |  College level, Elementary level, energy, experiments, High School level, Middle School level, Physics | Tagged: awesome science experiment, discrepant event, F=MA, kinetic energy, PBL, phenomenon based learning, shock waves, smashing steel spheres, thermal energy, thermite reactions |
College level, Elementary level, energy, experiments, High School level, Middle School level, Physics | Tagged: awesome science experiment, discrepant event, F=MA, kinetic energy, PBL, phenomenon based learning, shock waves, smashing steel spheres, thermal energy, thermite reactions |  Permalink
Permalink
 Posted by Tami O'Connor
Posted by Tami O'Connor
June 12, 2010
 by: Martin Sagendorf
by: Martin Sagendorf
This 3D Magnetic Field demonstration is actually quite easy to do. It clearly illustrates that magnetic fields are not flat (as too frequently demonstrated in the classroom).
Demonstrating a 3D Magnetic Field
This easy-to-make construction requires only four components:
- A clear plastic bottle (about 1-3/4” in one dimension) – the one illustrated below is a 12.6 fl oz ultra concentrated Joy ® dishwashing soap bottle – Note that any bottle originally containing soap or detergent will require repeated rinses to completely remove all of its original contents.

- Six 17 mm x 3 mm Neodymium ring magnets Read the rest of this entry »
 Leave a Comment » |
Leave a Comment » |  Elementary level, experiments, magnetism, Middle School level, Physics | Tagged: fun experiments, magnetic fields, magnets, phenomenon based learning |
Elementary level, experiments, magnetism, Middle School level, Physics | Tagged: fun experiments, magnetic fields, magnets, phenomenon based learning |  Permalink
Permalink
 Posted by Tami O'Connor
Posted by Tami O'Connor
June 11, 2010
 by: Michelle Bertke
by: Michelle Bertke
Simple iron filings can be used for a variety of interesting experiments and demonstrations. Magnetism is a mysterious concept that can be difficult for students to grasp. Magnetic fields are the forces surrounding a magnet that are identified by how they interact with adjacent magnets and other metal objects. While magnetic fields are ‘invisible’ they can be observed by sprinkling iron filings on a white paper with magnets beneath.
Read the rest of this entry »
 Leave a Comment » |
Leave a Comment » |  Elementary level, experiments, magnetism | Tagged: fun experiments, iron filings, magnetic fields, magnetism, phenomenon based learning |
Elementary level, experiments, magnetism | Tagged: fun experiments, iron filings, magnetic fields, magnetism, phenomenon based learning |  Permalink
Permalink
 Posted by Tami O'Connor
Posted by Tami O'Connor
 by: Tami O’Connor
by: Tami O’Connor In demonstrations of liquids of varying densities, the liquid with the greatest density will sink to the bottom of the container while the less dense liquid will remain on the top. There are wonderful demonstrations you can conduct with your class using immiscible liquids (liquids that do not mix) of different densities, and there are a number of high interest experiments your students can conduct using liquids of different densities. If you find this topic interesting, please visit the blog we wrote on the W-Tube.
In demonstrations of liquids of varying densities, the liquid with the greatest density will sink to the bottom of the container while the less dense liquid will remain on the top. There are wonderful demonstrations you can conduct with your class using immiscible liquids (liquids that do not mix) of different densities, and there are a number of high interest experiments your students can conduct using liquids of different densities. If you find this topic interesting, please visit the blog we wrote on the W-Tube.
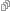

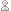 Posted by Tami O'Connor
Posted by Tami O'Connor 

 by: Martin Sagendorf
by: Martin Sagendorf
