 by: Tami O’Connor
by: Tami O’Connor
Density is not typically an easy concept for most middle school students and even more difficult for younger students, but it doesn’t need to be. We all know that D=m/V, but the easiest way I found to explain it to my students was to have them visualize a common dilemma in my home immediately preceding a vacation. For years, as a poor starving teacher, I only had one suitcase, and it was actually a hand-me-down from my mother. It was a medium sized Samsonite, hard cased piece of luggage. When approaching the topic of density in my classroom, down from the attic it came.
My explanation began with an imaginary week-long summer vacation to a low-key resort. The class and I would brainstorm the items I needed to pack for my trip. Generally, the list included items such as a few bathing suits, shorts, t-shirts, a pair of flip flops, some PJs, underwear and a few toiletries. It was obvious by looking at the size of my suitcase that in addition to my meager belongings, I could have probably also fit one of my students in my bag… ok, perhaps one of the smaller kids.
I explained that when I closed the suitcase, it was hard to see, simply by looking at it, how heavy it was. The lesson didn’t stop there. We now planned my one-week ski vacation to Vermont during the February break. Once again, my students and I made up my pack list. The list included a couple of heavy sweaters, long johns, gloves, a hat, boots… as you can imagine, the list went on and on. The question was, where to put it all. Of course, since I had only one suitcase, the answer was easy. Read the rest of this entry »
 Every Dark Spoon has a Silver Lining – Using Chemistry on Silver Tarnish
Every Dark Spoon has a Silver Lining – Using Chemistry on Silver Tarnish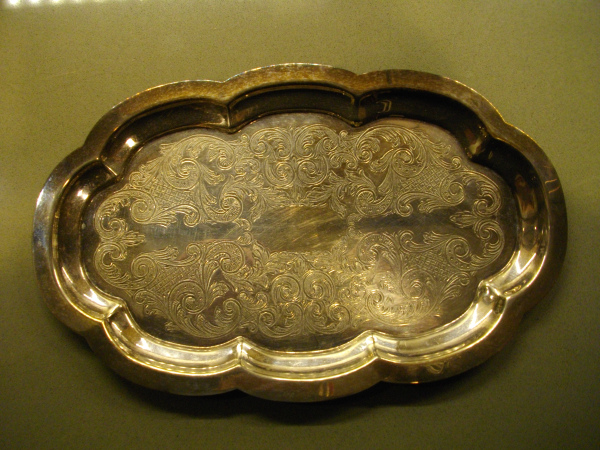


 Posted by Tami O'Connor
Posted by Tami O'Connor  by: John Fedors
by: John Fedors
 by: Tami O’Connor
by: Tami O’Connor


 by: Norman Barstow
by: Norman Barstow